One Health Evidence Inbox

Wildlife Trade, Pandemics and the Law: Fighting this year's virus with last year's law
This paper is the follow-up to a brief survey of legislation conducted by Legal Atlas in June of 2020 on existing legal approaches to controlling zoonotic disease risk in the context of wildlife trade.

Reducing Public Health Risks Associated with the Sale of Live Wild Animals of Mammalian Species in Traditional Food Markets
Traditional food markets, rather than supermarkets, are the norm in many parts of the world.

Veterinary Intelligence: Integrating Zoonotic Threats into Global Health Security
Zoonotic diseases are leading threats to public health globally.

The United Nations Sustainable Development Goals on Biodiversity, Climate Change and Health Agenda
A stable climate and healthy ecosystems provide the basic underpinnings of human welfare and development.

Preventing the Next Pandemic -- Zoonotic Disease and How to Break Chain of Transmission
This report is one of the first that specifically focuses on the environmental side of the zoonotic dimension of disease outbreaks during the COVID-19 pandemic.

Situation Analysis: COVID-19, Wildlife Trade, and Consumer Engagement
Despite evidence still being unclear as to the origins of the virus, people’s relationship with and consumption of wild animals such as pangolins has been irreversibly cast into sharp relief.

Ecological Interventions to Prevent and Manage Zoonotic Pathogen Spillover
Spillover of a pathogen from a wildlife reservoir into a human or livestock host requires the pathogen to overcome a hierarchical series of barriers.

The Security Threat that Binds Us: The Unraveling of Ecological and Natural Security and What the United States Can Do About It
Global ecological disruption is arguably the 21st Century’s most underappreciated security threat.

Report of the Scientific Task Force on Preventing Pandemics
The report contains key findings and recommendations for research and action to inform pandemic prevention.

Ecological Countermeasures for Preventing Zoonotic Disease Outbreaks: When Ecological Restoration is a Human Health Imperative
Ecological restoration should be regarded as a public health service.

Forests Moderate the Effectiveness of Water Treatment at Reducing Childhood Diarrhea
Environmental degradation has been associated with increased burden of diseases such as malaria, diarrhea, and malnutrition.

Post COVID-19: A Solution Scan of Options for Preventing Future Zoonotic Epidemics
The crisis generated by the emergence and pandemic spread of COVID-19 has thrown into the global spotlight the dangers associated with novel diseases, as well as the key role of animals, especially wild animals, as potential sources of pathogens to humans.

Land Use-Induced Spillover: A Call to Action to Safeguard Environmental, Animal, and Human Health
The rapid global spread and human health impacts of SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, show humanity’s vulnerability to zoonotic disease pandemics.

PAHO One Health: A Comprehensive Approach for Addressing Health at the Human-Animal-Environment Interface
The aim of this policy on One Health is to foster coordination and collaboration among the different governance frameworks of human, animal, plant, and environmental health programs in order to better prevent and prepare for current and future health challenges at the human-animal-environment interface.

A Rapid Review of Evidence on Managing the Risk of Disease Emergence in Wildlife Trade
This synthesis integrates the lessons learned from each of the report’s chapters and highlights their implications for planning an OIE program on the wildlife trade and emerging infectious diseases.

Training Manual on Wildlife Diseases and Surveillance
The OIE launched a global programme of capacity building for OIE Delegates and OIE Focal Points on different topics in 2009.

Biodiversity and the Economic Response to COVID-19: Ensuring a Green and Resilient Recovery
This Policy Brief focuses on the vital role of biodiversity for human life and the importance of integrating biodiversity considerations into the recovery from the COVID-19 crisis.

Live and Wet Markets: Food Access versus the Risk of Disease Emergence
Emerging zoonotic diseases exert a significant burden on human health and have considerable socioeconomic impact worldwide.

Biodiversity and Health in the Urban Environment
A key research gap is to understand—and evidence—the specific causal pathways through which biodiversity affects human health.

Gaps in Health Security Related to Wildlife and Environment Affecting Pandemic Prevention and Preparedness
Improved health security is crucial for global and national health systems to counter infectious disease epidemics and their wide-scale socioeconomic consequences.

Amazon Deforestation Drives Malaria Transmission, and Malaria Burden Reduces Forest Clearing
Deforestation and land use change are among the most pressing anthropogenic environmental impacts.

A Comparison of Three Holistic Approaches to Health: One Health, EcoHealth, and Planetary Health
Several holistic and interdisciplinary approaches exist to safeguard health.

Global Shifts in Mammalian Population Trends Reveal Key Predictors of Virus Spillover Risk
Emerging infectious diseases in humans are frequently caused by pathogens originating from animal hosts, and zoonotic disease outbreaks present a major challenge to global health.

Drivers of Antibiotic Resistance Transmission in Low-and Middle-Income Countries from a One Health Perspective - A Review
Antibiotic resistance is an ecosystem problem threatening the interrelated human-animal-environment health under the “One Health” framework.

IPBES Workshop on Biodiversity and Pandemics
Pandemics represent an existential threat to the health and welfare of people across our planet.
Intersectoral collaboration shaping One Health in the policy agenda_Ghana and India.pdf
Intersectoral collaborations are an integral component of the prevention and control of diseases in a complex health system.

Information About Zoonotic Disease Risks Reduces Desire to Own Exotic Pets Among Global Consumers
Demand for exotic pets is a substantial driver of the illegal wildlife trade.

Coronavirus Testing Indicates Transmission Risk Increases along Wildlife Supply Chains for Human Consumption in Viet Nam
Outbreaks of emerging coronaviruses in the past two decades and the current pandemic of a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) that emerged in China highlight the importance of this viral family as a zoonotic public health threat.

How to Start Up a National Wildlife Health Surveillance Programme
A sound understanding of wildlife health is required to inform disease management and mitigation measures in order to help safeguard public, livestock, companion animal and wildlife health.

The Berlin Principles on One Health - Bridging Global Health and Conservation
For over 15-years, proponents of the One Health approach have worked to consistently interweave components that should never have been separated and now more than ever need to be re-connected: the health of humans, non-human animals, and ecosystems.

Ranking the Risk of Animal-to-Human Spillover for Newly Discovered Viruses
The death toll and economic loss resulting from the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic are stark reminders that we are vulnerable to zoonotic viral threats.

The Evolution of One Health: A Decade of Progress and Challenges for the Future
In the early years of the 21st century, emerging zoonotic viruses that had the potential to cause pandemic disease, including extensive human mortality, created several international crises (Gibbs 2005).

A Global Deal for our Pandemic Age: Report of the G20 High Level Independent Panel on Financing the Global Commons for Pandemic Preparedness and Response
The High Level Independent Panel was asked by the G20 in January 2021 to propose how finance can be organized, systematically and sustainably, to reduce the world’s vulnerability to future pandemics.

Taking a Multisectoral, One Health Approach: A Tripartite Guide to Addressing Zoonotic Diseases in Countries
Every day we hear about health challenges at the human-animal-environment interface.

Technical guidelines on rapid risk assessment for animal health threats
When an imminent threat or emergency arises from an animal health event, it is important to conduct a rapid risk assessment (RRA) that informs animal health decision-makers of the most efficient control measures that they can take to control the disease concerned.

One Health legislation: Contributing to pandemic prevention through law
The COVID-19 pandemic and other emerging infectious diseases, as well as the continuing threat of antimicrobial resistance (AMR), are reminding us of the close connections between human, animal and environmental health and the urgent need to address them in a holistic manner.

Does deforestation drive visceral leishmaniasis transmission? A casual analysis
Vector-borne diseases (VBDs) are important contributors to the global disease burden and are a key factor in perpetuating economic inequality.

Developing a One Health Approach by Using a Multi-Dimensional Matrix
The One Health concept that human, animal, plant, environmental, and ecosystem health are linked provides a framework for examining and addressing complex health challenges.

Compendium of WHO and other UN Guidance on Health and Environment
The World Health Organization (WHO) and other United Nations (UN) organizations have published extensive guidance on a range of essential health topics over the years, specifically addressing disease, environmental pollutants, children’s health, among many other topics.
Climate Change-Triggered Land Degredation and Planetary Health: A Review
Land is a vital natural resource for human socio-ecological wellbeing.

Biodiversity and Human Health Interlinkages in Higher Education Offerings: A First Global Overview
Biodiversity is inextricably linked to human health.
A One Health Glossary to Support Communication and Information Exchange Between Human Health, Animal Health and Food Safety Sectors
Collaboration across sectors, disciplines and countries is a key concept to achieve the overarching One Health (OH) objective for better human, animal and environmental health.
Small Mammal Glucocorticoid Concentrations vary with Forest Fragment Size, Trap Type, and Mammal Taxa in the Interior Atlantic Forest
Species that live in degraded habitats often show signs of physiological stress.
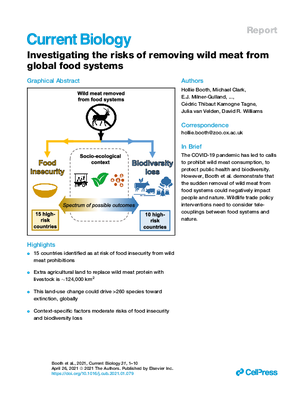
Investigating the Risks of Removing Wild Meat from Global Food Systems
The COVID-19 pandemic has led to calls to prohibit wild meat consumption, to protect public health and biodiversity.
A Tool for Rapid Assessment of Wildlife Markets in the Asia-Pacific Region for Risk of Future Zoonotic Disease Outbreaks
Decades of warnings that the trade and consumption of wildlife could result in serious zoonotic pandemics have gone largely unheeded.

Global Hotspots and Correlates of Emerging Zoonotic Diseases
Zoonoses originating from wildlife represent a significant threat to global health, security and economic growth, and combatting their emergence is a public health priority.

Disease Risk from Human-Environment Interactions: Environment and Development Economics for Joint Conservation-Health Policy
Emergence of COVID-19 joins a collection of evidence that local and global health are infuenced by human interactions with the natural environment.

Opportunities for Transdisciplinary Science to Mitigate Biosecurity Risks from the Intersectionality of Illegal Wildlife Trade with Emerging Zoonotic Pathogens
Existing collaborations among public health practitioners, veterinarians, and ecologists do not sufficiently consider illegal wildlife trade in their surveillance, biosafety, and security (SB&S) efforts even though the risks to health and biodiversity from these threats are significant.

A Framework to Guide Planetary Health Education
People around the world are increasingly facing the pressing challenges of today's interconnected environmental, social, and health crises.

A Better Classification of Wet Markets is Key to Safeguarding Human Health and Biodiversity
Wet markets have been implicated in multiple zoonotic outbreaks, including COVID-19.

Aquaculture at the Crossroads of Global Warming and Antimicrobial Resistance
In many developing countries, aquaculture is key to ensuring food security for millions of people.

The Right to a Healthy Environment: Reconceptualizing Human Rights in the Face of Climate Change
There is hardly any doubt that climate change threatens the enjoyment of a wide range of human rights.
CHANS-Law: Preventing the Next Pandemic through the Integration of Social and Environmental Law
Zoonotic viruses have sacrifced hundreds of millions of people throughout human history.

Strengthening Health Security Across the Globe: Progress and Impact of United States Government Investments in the Global Health Security Agenda
In 2020, the United States partnered with over 40 countries, including 19 Global Health Security Agenda (GHSA) countries (called Intensive Support countries) described in this report, to provide operational and technical assistance to build their health security capacities.

Land-based Measures to Mitigate Climate Change: Potential and Feasibility by Country
Land-based climate mitigation measures have gained significant attention and importance in public and private sector climate policies.

Land-use Change and Rodent-borne Diseases: Hazards on the Shared Socioeconomic Pathways
Land-use change has a direct impact on species survival and reproduction, altering their spatio-temporal distributions.

Wild Animal and Zoonotic Disease Risk Management and Regulation in China: Examining gaps and One Health opportunities in scope, mandates, and monitoring systems
Emerging diseases of zoonotic origin such as COVID-19 are a continuing public health threat in China that lead to a significant socioeconomic burden.

Outbreaks of Vector-Borne and Zoonotic Diseases are Associated with Changes in Forest Cover and Oil Palm Expansion at Global Scale
Deforestation is a major cause of biodiversity loss with a negative impact on human health.

One Health and the Environment: From Conceptual Framework to Implementation Science
The insignia of several agencies dedicated to health and healing depict an animal, a snake, coiled around a potent staff.

One Welfare Impacts of COVID-19 - A Summary of Key Highlights within the One Welfare Framework
One Welfare describes the interconnection between animal welfare, human wellbeing and their physical and social environment.

Role of Pollution on the Selection of Antibiotic Resistance and Bacterial Pathogens in the Environment
There is evidence that human activity causes pollution that contributes to an enhanced selection of bacterial pathogens in the environment.

Strategies for Implementing a One Welfare Framework into Emergency Management
During emergencies, people’s decision-making and actions are strongly influenced by their relationship with their animals.

The COVID-19 Pandemic is Intricately Linked to Biodiversity Loss and Ecosystem Health
The ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, caused by zoonotic SARS-CoV-2, has important links to biodiversity loss and ecosystem health.

The Impact of Climate Change on Health: Reducing Risks and Increasing Resilience in the Era of COVID-19
The climate crisis has many consequences – among them widespread health impacts that will lead to immense societal, ecological, and economic harm.

Working Together to Protect Australia in the Age of Pandemics
The COVID-19 pandemic has infiltrated every level of social, cultural and political life and has demonstrated the truly devastating effects of ineffective pandemic management systems.

A Systems Approach to Evaluate One Health Initiatives
Challenges calling for integrated approaches to health, such as the One Health (OH) approach, typically arise from the intertwined spheres of humans, animals, and ecosystems constituting their environment.

Improving rural health care reduces illegal logging and conserves carbon in a tropical forest
Tropical forest loss currently exceeds forest gain, leading to a net greenhouse gas emission that exacerbates global climate change.

International law reform for One Health notifications
Epidemic risk assessment and response relies on rapid information sharing.

Manual for the management of operations during an animal health emergency
This manual provides guidelines for countries and relevant local, national, regional and international organizations to prepare for and manage operations during animal health emergencies.

Guidance on mainstreaming biodiversity for nutrition and health
While human ingenuity and innovation have made considerable strides in meeting growing demands for food, shelter and energy over the past century, this progress has carried very high social and environmental costs (1).

Practical Actions to Operationalize the One Health Approach in the Asian Development Bank
One Health is an approach to human, animal, plant, and ecological health challenges that starts from a simple premise: these are all interconnected, and their solution demands communication, coordination, and collaboration across multiple sectors, disciplines, and levels of government.

Good emergency management practice: The essentials
Animal health emergencies arising from infectious diseases and other threats have a high potential to spread rapidly within a country or around the world.

Pollution and health: a progress update
The Lancet Commission on pollution and health reported that pollution was responsible for 9 million premature deaths in 2015, making it the world’s largest environmental risk factor for disease and premature death.

Antimicrobial Resistance and Environmental Health: A Water Stewardship Framework for Global and National Action
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is a global health crisis that affects all life on Earth.

Extend Existing Food Safety Systems to the Global Wildlife Trade
This article discusses the suspected role of the wildlife trade in the COVID-19 pandemic and the risk of new emerging infectious diseases in humans have received widespread attention since the emergence of COVID-19.

Predicting the Potential for Zoonotic Transmission and Host Associations for Novel Viruses
Host-virus associations have co-evolved under ecological and evolutionary selection pressures that shape cross-species transmission and spillover to humans.
Effectiveness of Front Line and Emerging Fungal Disease Prevention and Control Interventions and Opportunities to Address Appropriate Eco-Sustainable Solutions
Fungal infections represent an under recognized threat to public health and antifungal resistance is increasing globally.

Effectiveness and Profitability of Preventive Veterinary Interventions in Controlling Infectious Diseases of Ruminant Livestock in Sub-Saharan Africa: A Scoping Review
Agriculture in general, and livestock production in particular, serve as a livelihood source for many people in sub-Saharan Africa.

Wildlife Susceptibility to Infectious Diseases at Global Scales
Disease transmission prediction across wildlife is crucial for risk assessment of emerging infectious diseases.
Roadmap for Achieving Net‑Zero Emissions in Global Food Systems by 2050
Food systems (FSs) emit about 20 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent per year (~ 35% of global greenhouse gas emissions).

Amphibian Collapses Increased Malaria Incidence in Central America
Biodiversity in ecosystems plays an important role in supporting human welfare, including regulating the transmission of infectious diseases.

Disease Control Tools to Secure Animal and Public Health in a Densely Populated World
Animal health is a prerequisite for global health, economic development, food security, food quality, and poverty reduction, while mitigating against climate change and biodiversity loss.
The Future of Fungi: Threats and Opportunities
The fungal kingdom represents an extraordinary diversity of organisms with profound impacts across animal, plant, and ecosystem health.

Integrated Pest Management (IPM) and One Health - A Call for Action to Integrate
One Health (OH) has gained considerable prominence since the beginning of the 21st century, among others, driven by the recent epidemics and the increasing importance of zoonotic diseases but most emphasis has been on the interactions between animal and human health, with considerably less attention to environmental and plant health.

Immediate Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic on the Use of Wildlife as Food Among Indigenous People and Local Communities in South America
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a range of effects on the environment and particularly on wildlife, through diverse and sometimes contradictory impact pathways.

Aligning Conservation and Public Health Goals to Tackle Unsustainable Trade of Mammals
Unsustainable wildlife trade is a major driver of biodiversity loss and an important public health threat.

Changing Food Systems and Infection Disease Risks in Low-Income and Middle-Income Countries
The emergence of COVID-19 has drawn the attention of health researchers sharply back to the role that food systems can play in generating human disease burden.

One Health Joint Plan of Action (2022-2026): Working Together for the Health of Humans, Animals, Plants and the Environment
The One Health Joint Plan of Action outlines the commitment of the four organizations – the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), the World Organization for Animal Health (WOAH, founded as OIE), and the World Health Organization (WHO) – to collectively advocate and support the implementation of One Health.

Research and Innovation Opportunities to Improve Epidemiological Knowledge and Control of Environmentally Driven Zoonoses
While zoonotic diseases are defined by transmission processes between animals and humans, for many of these diseases the presence of a contaminated environmental source is the cause of transmission.

One Health for All: Advancing Human and Ecosystem Health in Cities by Integrating an Environmental Justice Lens
The One Health concept provides an organizing framework that promotes the health and well-being of urban communities and ecosystems.

One Health High-Level Expert Panel: One Health Theory of Change
The OHHLEP, established in May 2021, provides an advisory function to the Quadripartite organizations – FAO, UNEP, WHO and WOAH – to support their provision of evidence-based scientific and policy advice and technical support on One Health-related matters to their members.
The Association Between Dengue Case and Climate: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Although previous research frequently indicates that climate factors impact dengue transmission, the results are inconsistent.

Climate Change Impacts on Plant Pathogens, Food Security, and Paths Forward
Plant disease outbreaks pose significant risks to global food security and environmental sustainability worldwide, and result in the loss of primary productivity and biodiversity that negatively impact the environmental and socio-economic conditions of affected regions.

Environmental Variation Across Multiple Spatial Scales and Temporal Lags Influences Hendra Virus Spillover
Pathogens can spill over and infect new host species by overcoming a series of ecological and biological barriers.

The Most At-Risk Regions in the World for High-Impact Heatwaves
Heatwaves are becoming more frequent under climate change and can lead to thousands of excess deaths.

Mainstreaming Zoonotic Spillover Prevention at Source in National Action Planning for Health Security in Line with the Core Focus of One Health
Excessive human-animal interactions are driven by ecosystem degradation.

Global Governance for Pandemic Prevention and the Wildlife Trade
Although ideas about preventive actions for pandemics have been advanced during the COVID-19 crisis, there has been little consideration for how they can be operationalized through governance structures within the context of the wildlife trade for human consumption.

Helping to Heal Nature and Ourselves Through Human-Rights-Based and Gender-Responsive One Health
The health of our planet and humanity is threatened by biodiversity loss, disease, and climate crises.

Operational Framework for Strengthening Human, Animal, and Environmental Public Health Systems at their Interface
Public health systems are impacted by, and must respond to, significant threats at the human-animal-environment interface.

Reducing Pandemic Risks at Source: Wildlife, Environment, and One Health Foundations in East and South Asia
Emerging infectious diseases (EIDs) are infections associated with new or significantly-expanded geographic scope or spread of zoonotic, vector-borne, and drug-resistant pathogens.

Academic Health Institutions’ Declaration on Planetary Health
This Declaration endorses the definition of planetary health as defined by the Planetary Health Alliance: Planetary health is a solutions-oriented, transdisciplinary field and social movement focused on analyzing and addressing the impacts of human disruptions to Earth’s natural systems on human health and all life on Earth.

Medicinal Plants Against Antimicrobial Resistance
The causes of antimicrobial resistance are complex.

Insects as Feed for Livestock Production
This review explains how the use of insects as livestock feed can improve sustainability of livestock production because insects can transform low value organic wastes into high quality feed.

Rice-Animal Co-Culture Systems Benefit Global Sustainable Intensification
Through a global consensus by synthesizing evidence from existing literature, this study found that rice-animal co-culture systems could produce more diverse food types and nutrient sources, enhance resource use efficiency and reduce methane emissions, while increasing farmers' income.

Protecting Brazilian Amazon Indigenous Territories Reduces Atmospheric Particulates and Avoids Associated Health Impacts and Costs
Indigenous territories are important for conservation, but little is known about their role in maintaining human health.

Seaweed’s Contribution to Food Security in Low- and Middle-Income Countries: Benefits from Production, Processing, and Trade
This paper explores the potential of seaweed to address food insecurity and poor nutrition, alongside its potential to mitigate the carbon footprint of food systems globally.

From Reacting to Preventing Pandemics - Building Animal Health and Wildlife Systems for One Health in East Asia and Pacific
The reduction of pandemic risk is a quintessential global public good and risk management that requires whole-of-society to respond to the pandemics at the country, regional, and global levels.

Human Disturbance Increases Coronavirus Prevalence in Bats
Human land modification is a known driver of animal-to-human transmission of infectious agents (zoonotic spillover).

What Climate-Smart Agriculture Means for Smallholder Farmers
Smallholder farmers generate an estimated 32 percent of global greenhouse-gas (GHG) emissions from agriculture and are one of the populations most at risk from climate change.

Improving the Assessment of Ecosystem and Wildlife Health: Microbiome as an Early Indicator
Human activities are causing dramatic declines in ecosystem health, compromising the functioning of the life-support system, economic activity, and animal and human health.

Evolution and Expansion of the One Health Approach to Promote Sustainable and Resilient Health and Well-being: A Call to Action
To ensure the One Health approach can function effectively within the new global context of converging health, economic, and ecological crises, it must evolve and expand.

Synthesis Report on the Environmental and Health Impacts of Pesticides and Fertilizers and Ways to Minimize Them
This report presents a comprehensive review of available information on environmental and health effects impacts of pesticides and fertilizers, and provides actions to be taken by stakeholders to minimize the adverse impacts.

Financial Incentives Often Fail to Reconcile Agricultural Productivity and Pro-Conservation Behavior
Paying resource users to preserve features of their environment could in theory better align production and conservation goals.

Sector Environmental Guideline: Livestock Production
The purpose of this document and the Sector Environmental Guidelines overall is to support environmentally sound design and management of USAID development activities by providing concise, plain-language information about the potential for beneficial impacts from well-managed livestock systems, the typical adverse environmental impacts of activities in the sector, how to prevent or otherwise mitigate adverse impacts, and how to minimize vulnerability of activities to climate change.

Prevention of Zoonotic Spillover: From Relying on Response to Reducing the Risk at Source
This review suggests that reducing zoonotic spillover risk at the source is economically beneficial.

One Health Systems Strengthening in Countries: Tripartite Tools and Approaches at the Human-Animal-Environment Interface
Unexpected pathogen transmission between animals, humans and their shared environments can impact all aspects of society.

Synergising Tools for Capacity Assessment and One Health Operationalisation
Multisectoral, One Health collaboration is essential for addressing national and international health threats that arise at the human–animal–environment interface.

Mitigating Zoonotic Disease Threats to Prevent Future Pandemics: A Critical Analysis of Policy Favoring the Closures of Wildlife Markets in Latin America
This report challenges the efficacy of wildlife market closure policy by considering cultural, socioeconomic, and legal factors for the existence of wildlife market within megadiverse countries in Latin America.

Implementing Human Health as a Landscape Service in Collaborative Landscape Approaches
Landscape services have been found to foster collaboration among actors in social-ecological transitions towards a more sustainable landscape.

Effects of Climate-Related Risks and Extreme Events on Health Outcomes and Health Utilization of Primary Care in Rural and Remote Areas: A Scoping Review
Rural populations are at risk of climate-related impacts due to ecological and geographical determinants, potentially leading to greater morbidity and health utilization.

World Forests, Global Change, and Emerging Pests and Pathogens
Global changes play an important role in altering patterns of human, animal, and plant host–pathogen interactions and invasive pest species.

The Deep Prevention of Future Pandemics Through a One Health Approach: What Role For a Pandemic Instrument?
More than half of all known human pathogens have animal origin and a key question that has arisen in the wake of the COVID-19 crisis is: how can the risk of future pandemics emerging from the animal-human-ecosystems interface be reduced? This policy brief seeks to advance thinking and debate on this question by offering analysis on how a Pandemic Instrument could incorporate the One Health approaches to strengthen pandemic prevention, preparedness and response.

The Role of Social Vulnerability in Improving Interventions for Neglected Zoonotic Diseases: The Example of Kyasanur Forest Disease in India
Forest-based communities manage many risks to health and socio-economic welfare including the increasing threat of emerging zoonoses.

Harnessing Soil Biodiversity to Promote Human Health in Cities
This research stresses that reductions in urban soil biodiversity elevate risks to human health, but soil biodiversity can improve human health through pathways including suppressing pathogens, remediating soil, shaping a beneficial human microbiome and promoting immune fitness.

Re-Imagining One Health: A Perspective From Social Science
As human decisions and actions are the locus of One Health challenges, it is critical to understand how people perceive and act on these connections.

Systems Thinking and Practice: A Guide to Concepts, Principles, and Tools for FCDO and Partners
This guide offers an insight into the theoretical foundations, conceptual frameworks, and facilitation tools for adopting a systems mindset and putting it into practice.

Global Trends in Antimicrobial Use in Food-Producing Animals: 2020 to 2030
Use of antimicrobials in farming has enabled the growth of intensive animal production and helped in meeting the global increase in demand for animal protein.

Transformative Learning for a Sustainable and Healthy Future Through Ecosystem Approaches to Health
This paper presents insights from the work of the Canadian Community of Practice in Ecosystem Approaches to Health (CoPEH-Canada) and 15 years (2008–2022) of land-based, transdisciplinary, learner-centered, transformative learning and training.

Challenges and Successes of One Health in the Context of Planetary Health in Latin America and the Caribbean
Latin America faces significant challenges in the last decades due to the deep social inequality associated with environmental degradation and biodiversity loss that menace the integral health of the diverse socio-ecological systems.
Facilitating Implementation of the One Health Approach: A Definition of a One Health Intervention
To provide evidence of the impact of implementing the One Health approach and to assess the process outputs, a definition of a One Health intervention is required.

Biodiversity Data Supports Research on Human Infectious Diseases: Global Trends, Challenges, and Opportunities
Research on emerging infectious diseases may require the access to geographical and ecological data of multiple species.

One Health 2: A Global Analysis of One Health Networks and the Proliferation of One Health Collaborations
There has been a renewed focus on threats to the human–animal–environment interface as a result of the COVID-19 pandemic, and investments in One Health collaborations are expected to increase.

One Health 3: How Prepared is the World? Identifying Weaknesses in Existing Assessment Frameworks for Global Health Security Through a One Health Approach
The COVID-19 pandemic has exposed faults in the way we assess preparedness and response capacities for public health emergencies.

One Health 4: Global and Regional Governance of One Health and Implications for Global Health Security
The apparent failure of global health security to prevent or prepare for the COVID-19 pandemic has highlighted the need for closer cooperation between human, animal, and environmental health sectors.

Recommendations and Technical Specifications for Sustainable Surveillance of Zoonotic Pathogens Where Wildlife is Implicated
A science-based participatory process guided by EFSA identified 10 priority zoonotic pathogens for future One Health surveillance in Europe.

Advancing One Health: Updated Core Competencies
In this paper, a review of past and currently accepted One Health core competencies was conducted, with competence gaps identified.

Pollinator Deficits, Food Consumption, and Consequences for Human Health: A Modeling Study
Animal pollination supports agricultural production for many healthy foods, such as fruits, vegetables, nuts, and legumes, that provide key nutrients and protect against noncommunicable disease.

WildHealthNet: Supporting the Development of Sustainable Wildlife Health Surveillance Networks in Southeast Asia
Wildlife and wildlife interfaces with people and livestock are essential surveillance targets to monitor emergent or endemic pathogens or new threats affecting wildlife, livestock, and human health.

Social-ecological System Health in Transfrontier Conservation Areas to Promote the Coexistence Between People and Nature
The ProSuLi in Transfrontier Conservation Areas in southern Africa project engaged with four communities in three countries (Botswana, Mozambique and Zimbabwe) to identify, co-design, implement, and monitor livelihoods interventions that could improve well-being.

Operationalizing the Environment Health Nexus in Asia and the Pacific: A Policy Guide on Opportunities for Enhancing Health, Biodiversity, Food System and Climate Action
This policy guide aims to support policymakers and stakeholders in the Asia-Pacific region to address environment-health risks and safeguard human health and well-being while protecting ecosystems.

Gender Analysis for One Health: Theoretical Perspectives and Recommendations for Practice
This paper outlines the consultative workshop, ‘‘Women and One Health,’’ and highlights outcomes toward shared terminology and integration of frameworks from one health, gender analysis, and women in agriculture.

Gender Gap Reduction and the One Health Benefits
This paper proposes an ecological approach to find relationships between quantitative indicators of the gender gap dimension, the environmental performance index and the life expectancy at birth as summary of human health index in 155 countries.

The Determinants of Planetary Health: An Indigenous Consensus Perspective
A group of Indigenous scholars, practitioners, land and water defenders, respected Elders, and knowledge-holders came together to define the determinants of planetary health from an Indigenous perspective.

On the Possibility of Decolonising Planetary Health: Exploring New Geographies for Collaboration
This Viewpoint explores research in planetary health across holistic worldviews and western scientific approaches, based our examination of decolonising interventions in planetary health by exploring how global trajectories play out in British Columbia, Canada.

Wet Market Biosecurity Reform: Three Social Narratives Influence Stakeholder Responses in Vietnam, Kenya, and the Philippines
In 2020, Covid-19 led to global policy statements promoting bans and reforms to wet markets in Asia and Africa to prevent future pandemics.

Overcoming Resistance: The Expert Panel on Antimicrobial Availability
This report focuses on one aspect of a comprehensive solution to the growing threat of Antimicrobial resistance — encouraging the development and commercialization of novel antimicrobials through pull incentives that offer enhanced financial returns to manufacturers bringing qualifying antimicrobials to the Canadian market and, more importantly, to patients in Canada.

Advancing Integrated Governance for Health Through National Biodiversity Strategies and Action Plans
In 2022, 196 government parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity agreed to update and redesign their national biodiversity strategies and action plans (NBSAPs) by the end of 2024.

Investigating Infectious Organisms of Public Health Concern Associated with Wild Meat
The wild meat trade poses a significant threat to public health as it facilitates the spillover of zoonotic pathogens through high-risk activities such as the hunting, butchering, trade, and consumption of wild animals.

A Review on the Fate, Human Health and Environmental Impacts, and Regulation of Antibiotics Used in Aquaculture
Antibiotics have been a necessary component of animal husbandry and aquaculture since they were first used in clinical settings in the 1940s to meet the rising demand for foods generated from animals.

Summary for Policymakers: The Thematic Assessment Report on Invasive Alien Species and Their Control
The Invasive Alien Species Assessment explores how invasive alien species affect nature and people globally.
Using Integrated Wildlife Monitoring to Prevent Future Pandemics Through One Health Approach
In the One Health context, Integrated Wildlife Monitoring (IWM) merges wildlife health monitoring and host community monitoring to early detect emerging infections, record changes in disease dynamics, and assess the impact of interventions in complex multi-host and multi-pathogen networks.
Stratifying the Urban Matrix Using Zoning Laws: A Protocol for Bats and Their Pathogens
Urbanization implies important ecological changes in bat communities and in their intra and interspecific pathogen transmission.

The Social Costs of Keystone Species Collapse: Evidence From The Decline of Vultures in India
Scientific evidence suggests the Earth is undergoing a mass extinction of species, caused by human activity.
Does Land‑use and Land Cover Affect Vector‑borne Diseases? A Systematic Review and Meta‑analysis
To evaluate the impact of land-use and land-cover (LULC) on the transmission of VBDs, we conducted a systematic review of the existing literature on the global effects of land use on VBDs.

Tackling Antimicrobial Resistance by Integrating One Health and the Sustainable Development Goals
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has been identified as a leading threat to global public health.
Organising for One Health in a Developing Country
Globally, zoonotic diseases pose an enormous and growing public health challenge, and developing countries are at the epicenter of it.

One Health: We’re All Connected!
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has created this coloring book to offer parents, guardians, and educators an interactive way to talk to kids about how the health of people, animals, and the environment is all connected—known as One Health.
Evaluation of a Global Training Program in One Health communication
A global Train-the-Trainer Program, focused on improving the communication techniques of One Health advocates, is assessed and evaluated in this study.

Association Between Particulate Matter Air Pollution and Clinical Antibiotic Resistance: A Global Analysis
This analysis is the first to describe the association between PM2·5 and clinical antibiotic resistance globally.

One Health and Neglected Tropical Diseases
One Health is defined as an approach to achieve better health outcomes for humans, animals, and the environment through collaborative and interdisciplinary efforts.

Guidance to Facilitate Monitoring and Evaluation for Antimicrobial Resistance National Action Plans
The aim of the the global action plan on antimicrobial resistance (AMR) is to ensure the continuity of successful treatment with effective and safe medicines.

Indigenous Determinants of Health: A Unified Call for Progress
Globally, substantial challenges remain for Indigenous Peoples.

Co-benefits of Marine Protected Areas for Nature and People
This research uses a statistical matching approach to examine whether marine protected areas are associated with co-benefits or trade-offs between reef fish abundances and measures of human well-being, including income, diet and food security in the Mesoamerican region.

A Planetary Health Innovation for Disease, Food and Water Challenges in Africa
Many communities in low- and middle-income countries globally lack sustainable, cost-effective and mutually beneficial solutions for infectious disease, food, water, and poverty challenges.

The Use of Environmental Scenarios to Project Future Health Effects: A Scoping Review
Environmental risks are a substantial factor in the current burden of disease, and their role is likely to increase in the future.

The values and risks of an Intergovernmental Panel for One Health to strengthen pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response
The COVID-19 pandemic has shown the need for better global governance of pandemic prevention, preparedness, and response and has emphasized the importance of organized knowledge production and uptake.

Operationalizing One Health in Pastoralist Settings Module 1: Principles and Applications of One Health
This facilitator guide is intended to help trainers deliver Module 1: Principles and Applications of One Health of the HEAL training package.

Characterizing the One Health Workforce to Promote Interdisciplinary, Multisectoral Approaches in Global Health Problem-solving
The objectives of this formative study were to build foundational knowledge of the One Health workforce regarding demographics, education, and employment, as well as to explore the benefits of One Health education to the workforce, the unique challenges that One Health workers face, and whether employers are satisfied with their employees working in One Health.

The Case for Investing in Animal Health to Support One Health
The Action for Animal Health coalition advocates for five pillars of action to secure animal health and welfare.
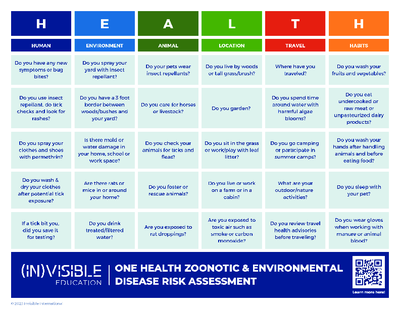
Zoonotic and Environmental Disease Risk Assessment Tool
This mnemonic device provides a matrix of questions to assess animal and environment disease risk.

One Health in Turkana County, Kenya: Applications and Lessons Learned
This case describes the development of the One Health Strategy in Turkana County, Kenya.

How Crop-livestock Clinics Are Advancing One Health: A Pilot Case from Uganda
This case narrates the early experiences with crop–livestock clinics – a novel, integrated advisory service for smallholder farmers, which is based on existing government extension structures and capacities.

Plastic Pollution: How Can the Global Health Community Fight the Growing Problem?
Plastic products and plastic waste threaten human health because of their toxicity, role in disease propagation, possible interference with food supply through their environmental effects and socioeconomic impacts.

Healthy Soil for Healthy Humans and a Healthy Planet
This review argues that a healthy soil is multifunctional and is capable of supporting human and planetary health.

WHO Guidance for Climate-resilient and Environmentally Sustainable Health Care Facilities
The aim of this guidance is to enhance the capacity of health care facilities to protect and improve the health of their target communities in an unstable and changing climate; and to empower health care facilities to be environmentally sustainable, by optimizing the use of resources and minimizing the release of waste into the environment.

Coastal Urbanization Influences Human Pathogens and Microdebris Contamination in Seafood
Seafood is one of the leading imported products implicated in foodborne outbreaks worldwide.

Mapping Potential Conflicts Between Global Agriculture and Terrestrial Conservation
Demand for food products, often from international trade, has brought agricultural land use into direct competition with biodiversity.

Progressive Management Pathway for Terrestrial Animal Biosecurity
FAO has pioneered the progressive management pathway (PMP) approach to assist countries, industries, and producers to gradually implement improved and sustainable levels of risk management.

Rights and Knowledge of Indigenous Peoples and Planetary Health
This Planetary Health Alliance (PHA) Policy Note aims to elevate the views expressed by Indigenous leaders in the 2023 UN Permanent Forum on Indigenous Issues (UNPFII) and call attention to how Planetary Health work can align with UNPFII.

The Effectiveness of Global Protected Areas for Climate Change Mitigation
Forests play a critical role in stabilizing Earth’s climate.

Importance of a One Health Approach in Advancing Global Health Security and the Sustainable Development Goals
The One Health community has faced difficulties in determining specific One Health impact indicators for formally evaluating One Health successes.

Opportunities and Challenges of Bio‐based Fertilizers Utilization for Improving Soil Health
Bio-based fertilizers (BBFs) have been promoted as a solution to help manage bio-waste problems and improve soil health conditions.

Improving the Ecological and Economic Performance of Agri-environment Schemes: Payment by Modelled Results Versus Payment for Actions
Researchers and policy-makers have become increasingly interested in re-designing agri-environmental policy to improve both economic efficiency and ecological effectiveness.

Pathogen Spillover Driven by Rapid Changes in Bat Ecology
During recent decades, pathogens that originated in bats have become an increasing public health concern.

One Health, Many Perspectives: Exploring Indigenous and Western Epistemologies
The objective of this project is to identify values in Indigenous science that are unsupported or underrepresented in Western science and then collaboratively ideate recommendations that Western allies can take to center and support Indigenous scientists and elevate Indigenous knowledge.

Evidence for Widespread Human Exposure to Food Contact Chemicals
Over 1800 food contact chemicals (FCCs) are known to migrate from food contact articles used to store, process, package, and serve foodstuffs.

Understanding How and Where Pathogens Emerge: Preparedness and Response for Zoonotic Diseases
This chapter will examine what we know about how and where zoonotic disease threats emerge and key gaps in the information needed for preparedness, both before an outbreak and in emergency response.
The Economic Impacts of Ecosystem Disruptions: Costs from Substituting Biological Pest Control
This work makes a contribution to our understanding of the relationship between ecosystem functioning and human well-being by using a natural experiment—an occurrence resulting from unexpected changes in environmental conditions that approximates a randomized control trial.

Planetary Health Learning Objectives: Foundational Knowledge for Global Health Education in an Era of Climate Change
In response to member demands for resources to support teaching and learning related to planetary health, the Consortium of Universities for Global Health (CUGH) convened a working group to develop a set of planetary health learning objectives (PHLOs) that would complement the existing ten CUGH global health learning objectives.

Navigating New Horizons: A Global Foresight Report on Planetary Health and Human Wellbeing
This Navigating New Horizons report outlines a process focused on planetary health and human wellbeing—an intentional framing to expand the range of issues and informed views that typically shape United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)’s work.

Surprising New Research Links Infant Mortality to Crashing Bat Populations
According to the research, published Thursday in the journal Science, farmers in affected U.

Where and How to Invest in Greenspace for Optimal Health Benefits: A Systematic Review of Greenspace Morphology and Human Health Relationships
Research on the relationship between greenspace morphology and health is a growing field that informs the spatial design of greenspace to enhance health outcomes.

Captive Wildlife Management Survey in Vietnam, 2015–2021
In Vietnam, breeding and raising a wide range of wildlife species in captive wildlife facilities are common practices but little information on the captive wildlife population is available.

African Union AMR Landmark Report: Voicing African Priorities on the Active Pandemic
Antimicrobial resistance (AMR) has emerged as a leading cause of death in the African region, surpassing fatalities from malaria, HIV, and TB.

Red Seaweed (Asparagopsis taxiformis) Supplementation Reduces Enteric Methane by Over 80 Percent in Beef Steers
The red macroalgae (seaweed) has shown to reduce ruminant enteric methane (CH4) production up to 99% in vitro.

To Handle Zoonoses Better, Indigenous People Must be Included in Policy Making
For a better One Health strategy, India needs to integrate indigenous knowledge with the scientific framework that guide national health policies.

A One Health Approach to Tackling AMR and Why Gender Matters: Findings from Pastoralist Communities in Tanzania
This paper focuses on the gendered risk of AMR through a study of gender and social determinants of access to and use of antimicrobials in low-resource pastoralist settings in Tanzania.
How Decline of Indian Vultures Led to 500,000 Human Deaths
More than two decades ago, India’s vultures began dying because of a drug used to treat sick cows.

Unfulfilled Promise: Pollinator Declines, Crop Deficits, and Diet-Associated Disease
In a new study in Environmental Health Perspectives, a team of scientists estimated effects of pollinator deficits on five diet-associated disease end points: stroke, cancer, type 2 diabetes, coronary heart disease, and all-cause mortality associated with changes in weight.

Climate Change Increases Cross-species Viral Transmission Risk
Changes in climate and land use will lead to opportunities for viral sharing among previously geographically isolated species of wildlife.
Plant Species Influences the Composition of Root System Microbiome and its Antibiotic Resistance Profile in a Constructed Wetland Receiving Primary Treated Wastewater
Constructed wetlands (CWs) are nature-based solutions for wastewater treatment where the root system microbiome plays a key role in terms of nutrient and pollutant removal.

Measuring and Monitoring Multi-Sectoral Nutrition Collaboration: Guidance and Considerations
USAID Advancing Nutrition developed guidance on measuring and monitoring multi-sectoral nutrition collaboration among organizations and partners to improve nutrition outcomes.

Global One Health Post-Graduate Programmes: A Review
In this study, an up-to-date repository of a subset of OH academic programs offered globally was provided, and their curricula contents was critically assessed.

One Health: Opportunities for Defence Engagement (Health)
This article explores how the One Health approach could and should be adopted within Defence Engagement (Health) activity to offer the potential for high-impact, low-risk activity while facilitating long-term relationship building.

Development Banks’ Joint Roadmap for Climate-Health Finance and Action
Through the Development Bank Working Group for Climate-Health Finance (the ‘Group’) in support of its clients, Development Banks will pursue a common strategy to maximize investments and impact at the climate-health nexus.

Guidelines for Addressing Disease Risks in Wildlife Trade
The Guidelines respond to a need to better manage risks from emerging diseases at the human–animal–environment interface, while protecting wildlife, through a One Health approach.

Information Brief: The Wildlife–Livelihoods–Health Nexus: Challenges and Priorities in Asia and the Pacific
This first information brief on the wildlife–livelihoods–health nexus in Asia and the Pacific is intended to shed light on the current landscape of human–wildlife–health interactions, examine the challenges, and the existing and potential opportunities for change.

Domestication Matters: Risk Analyses Necessary to Prevent Zoonotic Pathogen Spillover from International Wildlife Trade are Constrained by Terminology
This paper explores how the terms domesticated animals and wildlife are applied across US federal agencies, as well as the implications thereof.

The Rising Global Economic Costs of Invasive Aedes Mosquitoes and Aedes-borne Diseases
This research presents a comprehensive, global-scale synthesis of studies reporting the economic costs of mosquito transmitted viruses, spanning 166 countries and territories over 45 years.

Planetary Health: Roadmap and Action Plan
This practical document aims to support our work in partnership for a future supporting the health and wellbeing of all life on Earth.

An Integrated Inventory of One Health Tools: Mapping and Analysis of Globally Available Tools to Advance One Health
This report maps and analyzes available One Health tools and assesses their suitability to support One Health implementation, including the One Health Joint Plan of Action 2022–2026 (OH JPA).

Applications of Implementation Science in Integrated Conservation and Health Programs: Improved Learning to Achieve Environmental and Health Objectives
Rigorous research around integrated One Health programming is limited and/or in very early stages, especially concerning counterfactual-based studies focused on the effectiveness of integrated conservation and health programming, including those focused on the intersection of zoonosis spillover risk in the context of land-use change.

Early-stage Loss of Ecological Integrity Drives the Risk of Zoonotic Disease Emergence
This study updated the most comprehensive zoonotic emerging infectious diseases (EID) event database with the latest reported events to analyze the relationship between EIDs of wildlife origin (zoonoses) and various facets of ecological integrity.

Developing a Logic Model for Communication-Based Interventions on Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR)
In developing the Supporting the National Action Plan for AMR (SNAP-AMR) Logic Model, we reviewed relevant communication theories to create and target messages, and we considered behavioral change theories.

Why One Health Needs More Social Sciences: Pandemic Prevention Depends on Behavior as well as Biology
This article argues the importance of mobilizing information and understanding across knowledge systems and elevate the critical role of social sciences to meaningfully integrate One Health into primary pandemic prevention in Canada.

Effectiveness of Greenhouse Gas Mitigation Intervention for Health-Care Systems: A Systematic Review
To identify evidence-based interventions that reduce greenhouse gas emissions in health-care systems, the authors systematically searched 11 electronic databases for articles published between 1990 and March 2023.

Putting Animals on the WASH Agenda - Policy Brief
This Policy Brief outlines to rationale for WASH interventions based on a good understanding of the roles, needs, and impacts of animals on water and sanitation and proposes possible pathways for action.

Current Evidence of the Economic Value of One Health Initiatives: A Systematic Literature Review
Funding and financing for One Health initiatives at country level remain challenging as investments commonly require demonstrated evidence of economic value or returns.

An Alarming Decline in the Nutritional Quality of Foods: The Biggest Challenge for Future Generations’ Health
This critical review emphasizes the importance of balance and adequate nutrition as well as the need to improve soil biodiversity and fertility.

Insights into the Reduction of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria and Mobile Antibiotic Resistance Genes by Black Soldier Fly Larvae in Chicken Manure
The bioconversion of animal manure with insect larvae, such as the black soldier fly larvae (BSFL), is a promising technology for quickly attenuating antibiotic-resistant bacteria while also recycling waste.

One Health in the Philippines: A Review and Situational Analysis
The Philippines faces a complex and interconnected web of human, animal, and environmental health issues, including zoonotic and reverse zoonotic diseases, antimicrobial resistance, food insecurity and contamination, and threats from environmental degradation.

Wake-up Call: Rapid Increase in Human Fungal Diseases Under Climate Change
Researchers are working to understand the factors, including climate change, driving the rise in invasive fungal diseases in people worldwide and how to reduce the threat.

Impacts of Climate Change on the Livestock Food Supply Chain: A Review of the Evidence
This article reviews the risk of climate-related impacts along the land-based livestock food supply chain, including processing operations, storage, transport, retailing and human consumption.
Assessment Report of the Status on the Nexus between Biodiversity and Health, Food and Nutrition, and Traditional Medicine in ASEAN Member States
This report aims to identify current policy priorities and joint implementation possibilities in the ASEAN Region across the sectors, identify best practices relating to knowledge use and implementation that can be appropriately replicated across the Region, with specific attention given to transboundary and collaborative arrangements, and lay a groundwork for a Policy Brief highlighting how the ACB may work with relevant ASEAN bodies.

European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control One Health Framework
This document describes a framework for how the European Centre for Disease Prevention and Control (ECDC) will strengthen, develop and implement the One Health approach in its activities for the prevention and control of communicable diseases in the European Union/European Economic Area (EU/EEA) in order to improve public health in the Member States.

A One Health Google Earth Engine Web‐GIS Application to Evaluate and Monitor Water Quality Worldwide
This study aimed to develop a Google Earth Engine app for indirect monitoring and assessment of water quality based on Sentinel-2 from a One Health perspective.

A Meta-Analysis on Global Change Drivers and the Risk of Infectious Disease
The authors reviewed literature that contains 2,938 observations of infectious disease responses to global change drivers across 1,497 host–parasite combinations, including plant, animal and human hosts.

One Health in Human-Environment Systems: Linking Health and the Sustainable Use of Natural Resources
The authors expand the social-ecological system (SES) approaches to One Health in Social-Ecological Systems (OHSES) by including humans as a resource system that contributes to the human capital of a nation’s gross domestic product (GDP).

U.S. Government Global Health Security Strategy 2024
This new Global Health Security Strategy lays out the actions the United States will take over the next 5 years to ensure continued this progress and deliver on the goals established in the 2022 National Biodefense Strategy and Implementation Plan, and the bipartisan Global Health Security and International Pandemic Prevention, Preparedness and Response Act of 2022.

Highlights Brief: WHO-IUCN Report On Designing Nature Based Solutions For Human Health
The purpose of the joint WHO-IUCN report is to break the silos between conservation, climate and health sectors, and explore the interplay between biodiversity conservation and global public health while highlighting how NbS can yield mutual benefits.

Interconnecting Global Threats: Climate Change, Biodiversity Loss, and Infectious Diseases
In this Review, the authors define and exemplify the causal pathways that link the three global pressures of climate change, biodiversity loss, and infectious disease.

Assessing Compounding Risks Across Multiple Systems and Sectors: A Socio-Environmental Systems Risk-Triage Approach
The research shares a unique “triage-based” visualization and data-sharing platform—the System for the Triage of Risks from Environmental and Socio-Economic Stressors (STRESS)—that brings together data across socio-environmental systems, economics, demographics, health, biodiversity, and infrastructure.

Immune-Mediated Disease Caused by Climate Change-Associated Environmental Hazards: Mitigation and Adaptation
Climate change is driving an increase in immune-mediated diseases such as asthma, allergies, autoimmune diseases, and cancers.
Assessment of Integrated Patterns of Human-Animal-Environment Health: A Holistic and Stratified Analysis
This paper uses the World Bank regional classification and the World Bank income groups to analyze the relationship between the Global One Health Index-One Health Intrinsic Drivers Index (GOH-IDI ) and regional economic levels, and completes the case studies of representative countries.
Potential Impacts of Pandemics on Global Warming, Agricultural Production, and Biodiversity Loss
In light of a rising frequency of infectious diseases, there is an urgent need to understand the ecological impacts of pandemics.

Ecological Countermeasures to Prevent Pathogen Spillover and Subsequent Pandemics
This resource explains the mechanisms linking environmental change and zoonotic spillover using spillover of viruses from bats as a case study.

Access to Human Health Benefits of Forests in Rural Low and Middle-Income Countries: A Literature Review and Conceptual Framework
Forests have been increasingly recognized for their beneficial contribution to human health, in addition to their established roles in biodiversity conservation, climate change mitigation, and poverty alleviation.

Impacts of Deforestation on Childhood Malaria Depend on Wealth and Vector Biology
This study analyzes the relationship between deforestation and malaria risk in children using a unique and large data set in six sub‐Saharan African countries.
Global One Health Index for Zoonoses: A Performance Assessment in 160 Countries and Territories
The One Health (OH) approach is used to control/prevent zoonotic events.

Regenerative Agriculture: A Literature Review on the Practices and Mechanisms Used to Improve Soil Health
Conventional farming practices can lead to soil degradation and a decline in productivity.

A One Health Framework for Integrated Service Delivery in Turkana County, Kenya
One Health approaches that integrate human and animal health service delivery can help to improve pastoralists’ health through increased vaccine coverage and improved access to services.

Reaping One Health Benefits Through Cross-sectoral Services
This chapter describes the added value of One Health through synergies created in delivering integrated healthcare services across health sectors.

Towards a One Health Assessment of Artisanal and Informal Mining in Benue State, Nigeria
This study evaluated the eco-health risk associated with exposure to lead in mining sites in Benue State, Nigeria.

Planetary Health Education in the United States: Four Curricular Models, One Goal
Global environmental crises demand scaled-up investment in education about planetary health.

An African One Health Network for Antimicrobial Resistance and Neglected Tropical Diseases
To best understand and tackle antimicrobial resistance (AMR), it is necessary to trace the linkages between human, animal, and environmental factors that contribute to AMR transmission via a One Health approach.

Defining Collaborative Surveillance: A Core Concept for Strengthening the Global Architecture for Health Emergency Preparedness, Response, and Resilience
This concept paper proposes an ambitious set of capabilities for strengthening evidence for public health decision-making.

Evidence for Policies and Practices to Address Global Food Insecurity
This review summarizes evidence for policies and practices across five elements of the agrifood system framework and identifies gaps that inform an agenda for future research.

One World, One Health: Exploring the Connectability between Human, Animal and Environmental Health
The purpose of our analysis was to better understand the stakeholders, influencers, key topics, and interaction shaping One Health conversations.

Soil Health Assessment and Spatial Characterization using Remote Sensing
This research summarizes recent developments in remote sensing (RS) approaches for measuring soil health and ecosystem services, their principles, and their future perspectives.

The Global Health Equity Atlas Releases a Decade of Data-Driven Insights in Pursuit of Health as a Fundamental Human Right
The Global Health Equity Atlas is an essential tool that consolidates over a decade of dedicated work in the field of global health equity.

Who Coined the Term “One Health”? Cooperation Amid the Siloization
This resource aims to describe the trajectory of the historical concept of "One Health.

Individual Differences in the Definitions of Health and Well-being and the Underlying Promotional Effect of the Built Environment
This study adopted a mixed-methods approach to investigate how “health” and “well-being” have been defined within the literature and in the community with the aim to clarify the definitions of those two terms further.

FAO in the 2024 Humanitarian Response Plans
This is a summary of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) work in providing food and resources to people in food crises.

Stakeholder Attitudes and Perspectives on Wildlife Disease Surveillance as a Component of a One Health Approach in Thailand
The aims of this study were to understand how wildlife disease surveillance in Thailand is utilized, valued, and can be improved within a One Health framework.


